
Newsletter Subscribe
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter

Oh, the internet! It’s supposed to be our window to the world, connecting us with grandkids, doctor’s appointments, and that endlessly fascinating cat video your neighbor shared.
But let’s be honest, sometimes it feels less like a window and more like a brick wall, doesn’t it? One minute you’re happily browsing, the next you’re staring at a “No Internet Connection” message that might as well be written in hieroglyphics.
You’re not alone in feeling that little pang of panic, or the urge to simply unplug everything and go back to carrier pigeons.
In fact, while 90% of adults aged 65 and over are online, a significant chunk—nearly 40% of older Americans—still grapple with getting reliable high-speed internet at home (Pew Research Center 2024 Survey; AgingConnected.org 2021).
It’s a frustrating dance, but one we can definitely master together.
This isn’t just about getting back online; it’s about understanding why things go wrong and feeling confident enough to fix them yourself.
Think of this article as your friendly tech co-pilot, guiding you through the ins and outs of Wi-Fi, routers, and all those mysterious blinking lights.
We’ll turn those internet conundrums into “aha!” moments, so you can spend less time troubleshooting and more time enjoying your digital life.
Feeling frustrated with your Wi-Fi? You’re certainly not alone. Many folks, especially those who didn’t grow up with a computer in their pocket, find internet issues overwhelming.
But here’s the good news: a lot of common problems have surprisingly simple solutions. This guide offers straightforward steps and clear explanations to get you connected again, no tech degree required. We’re here to help you solve it simply and quickly.
Analogy: The Internet Doctor’s Initial Checkup
When your car won’t start, the mechanic doesn’t immediately take the engine apart, right? They start with the basics: Is there gas? Is the battery connected? Your internet is much the same.
Before diving into complex diagnostics, there are three powerful, simple steps that solve a surprising number of internet woes. Think of these as your internet doctor’s initial checkup.
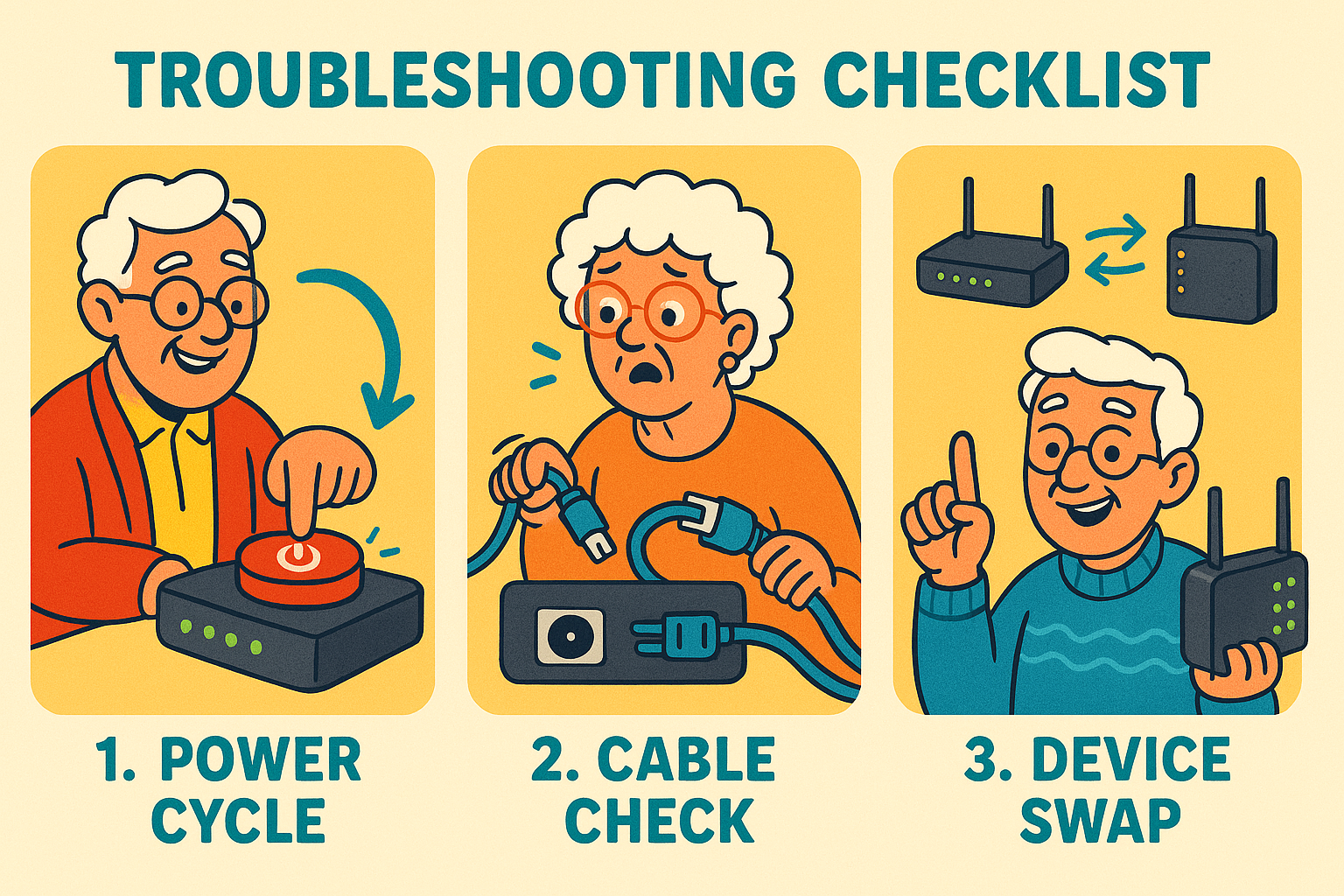
Troubleshooting Checklist 1: The “Power Cycle” (Restart Everything)
Why does “turning it off and on again” work so often? Well, imagine your electronic devices are like tiny brains constantly processing information. Sometimes, they just need a moment to clear their thoughts and reboot. A power cycle is like giving them a refreshing nap.
Actionable: Unplug both your modem (the box that brings internet into your home) AND your router (the box that shares it around your home). Wait a full 60 seconds.
Then, plug the modem back in first. Once its lights settle down (usually 1-2 minutes), plug your router back in.
Wait another 5 minutes for everything to fully reconnect. This simple trick often clears up hiccups.
Troubleshooting Checklist 2: The “Cable Check”
Think of your internet cables as tiny garden hoses carrying water. If there’s a kink, or if the hose isn’t fully connected, the water won’t flow properly. The same goes for your internet! A loose or damaged cable can bring your online adventures to a screeching halt.
Actionable: Gently wiggle every cable connected to your modem and router. Make sure they feel secure and “click” into place. Check for any obvious damage, like frayed wires or bent connectors. Sometimes, a tiny jostle is all it takes to get things flowing again.
Troubleshooting Checklist 3: The “Device Swap”
Is the problem with your internet connection itself, or just with the device you’re trying to use? This step helps us find out.
If only one device (like your laptop) can’t get online, but your phone or tablet can, then the problem is likely with that specific laptop, not your whole internet setup.
Actionable: Try connecting to the internet on another device. If your computer isn’t working, grab your smartphone or tablet and see if it can load a webpage.
If it works on another device, then you know your main internet connection is probably fine, and the issue lies with the original device.
Analogy: The Internet’s Front Door and the Home’s Mailroom
Let’s demystify those two boxes your internet service provider (ISP) gave you. They might look similar, but they have very different jobs. Imagine the internet as a vast, bustling highway system.
Your modem is like the special front door that connects your home directly to that big internet highway.
It translates the digital signals from your ISP (like cable, fiber, or DSL) into a language your devices can understand. Without it, your home is cut off from the outside world.
Your router, on the other hand, is like your home’s internal mailroom and traffic controller. Once the internet comes through the modem, the router takes that connection and efficiently shares it with all the devices inside your house—your computer, phone, tablet, smart TV, and so on.
It also creates your Wi-Fi signal, allowing devices to connect wirelessly.
Sometimes, you might have an all-in-one gateway, which is just a fancy name for a single device that combines both the modem and router functions. It’s like having your front door and mailroom rolled into one convenient package.
The key distinction? You need both functionalities (even if they’re in one box) for multiple devices and reliable Wi-Fi throughout your home.
Analogy: Traffic Lights for Your Internet
You know how traffic lights tell you what’s happening on the road? Your modem and router have their own set of “traffic lights” that can tell you a lot about your internet connection. Learning to read these lights is like getting a secret decoder ring for your home network.
Most devices will have a few key lights, and their colors or blinking patterns give clues (BroadbandSearch.net).
Actionable Advice for Each Light Status:
Analogy: Too Many Cars on a Small Road
Nothing’s more frustrating than internet that crawls along like a turtle, or drops out when you’re in the middle of a video call with the grandkids. Imagine your Wi-Fi signal as a road, and your data as cars. If the road is too narrow, too crowded, or has too many obstacles, things slow down or grind to a halt.
Common Causes Explained Simply:
Solutions: Get Your Wi-Fi Zooming Again!
If your router offers both, try connecting to the 5 GHz network if you’re close to the router and need speed.
Analogy: A Monthly Allowance for Your Internet Use
Many internet providers have something called a “data cap” or “data allowance.” Think of it like a monthly allowance for your internet use.
You get a certain amount of “data” (the information flowing in and out of your home) each month. If you go over, you might get charged extra or your internet speeds might slow down dramatically.
It’s like exceeding your phone plan’s data limit, but for your whole home internet.
What is a Data Cap?
It’s a limit set by your ISP on how much data you can download and upload in a billing cycle. While common for mobile plans, it’s becoming more prevalent for home internet too.
What Happens if You Exceed It?
Typically, your ISP will either slow down your internet speed significantly (this is called “throttling”) or charge you extra fees for “overages.” Neither is fun, so it’s good to be aware.
How Much Data Do You Need?
| Usage Tier | Typical Monthly Data | Common Activities | Best Plan Type | Household Size Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light User | 50–100 GB | Email, light browsing, occasional video calls | Low-cost cable/DSL or fixed wireless with modest data cap | 1 person or 1–2 light users |
| Moderate User | 200–500 GB | Regular browsing & social media; a few hours of streaming video daily | Cable or fiber; prefer higher data caps or soft‑unlimited | 2–4 people / several devices |
| Heavy User | 500 GB+ (often 1–2 TB+) | Frequent HD/4K streaming, online gaming, multiple simultaneous streams/devices | Fiber (best) or high‑tier cable with truly unlimited data | 3+ people / many devices & power users |
This varies widely!
Practical Tips for Seniors to Reduce Data Usage:
Analogy: A Short, Invisible Cord for Two Devices
Bluetooth is like a magical, invisible cord that connects two devices together over a short distance, without any messy wires! It’s fantastic for things like wireless headphones, portable speakers, or even some medical devices like hearing aids. You don’t need the internet for Bluetooth to work; it’s a direct connection between the devices themselves (AARP.org).
What is Bluetooth?
It’s a wireless technology that allows two Bluetooth-enabled devices to talk to each other when they’re close by, typically within about 30 feet.
Step-by-Step Pairing Guide (with Screenshots – Placeholder for visual guides, e.g., for iOS/Android):
Let’s use a smartphone as an example, as it’s a very common device for seniors.
Common Issues and Simple Fixes:
Analogy: Adding More Roads vs. Building a Whole New Highway System
Ever find that your Wi-Fi signal is strong in the living room, but practically non-existent in the bedroom or out on the patio?
That’s a common problem in larger homes or houses with thick walls. When your Wi-Fi signal can’t reach every corner, you have a couple of main options to extend its reach.
Wi-Fi Extenders: Adding More Roads
Mesh Wi-Fi Systems: Building a Whole New Highway System
Decision Guide for Seniors: When to Choose Which
Getting your internet back online is a fantastic achievement, but it’s also a great opportunity to think about staying safe and confident online in the long run.
Seniors are unfortunately a common target for online scams, with elder fraud complaints increasing significantly (FBI IC3 2025 via TheSeniorList.com). So, a little proactive thinking goes a long way.
Q: My internet light is blinking, but I still can’t get online. What does that mean?
A: A blinking internet light usually means your modem or router is trying to connect to your internet service provider, but it hasn’t quite locked on yet. Give it a few more minutes, especially after a restart. If it keeps blinking for an extended period (more than 5-10 minutes), it often indicates a problem with your ISP’s connection to your home, and it’s time to call them.
Q: Why does my Wi-Fi work fine on my phone but not my computer?
A: If one device works and another doesn’t, the problem is usually with the device that isn’t connecting, not your overall internet. Check your computer’s Wi-Fi settings to make sure it’s connected to the correct network and that Wi-Fi isn’t accidentally turned off. Sometimes, simply restarting the computer can fix it.
Q: Is it bad to leave my router and modem on all the time?
A: No, it’s generally fine and expected for them to be on all the time. They are designed for continuous operation. In fact, turning them off frequently can sometimes interrupt important updates or cause minor connection issues when they power back on. Only restart them when you’re actively troubleshooting a problem.
Q: What’s the difference between my Wi-Fi password and my router’s admin password?
A: Your Wi-Fi password (also called your network key or security key) is what you use to connect devices like your phone or tablet to your wireless network. Your router’s admin password is what you use to log into your router’s settings page (usually through a web browser) to change things like your Wi-Fi network name or other advanced settings. It’s important to keep both secure!
Q: Should I get a faster internet speed if my Wi-Fi is slow?
A: Not necessarily! If your Wi-Fi is slow due to poor signal strength, interference, or an old router, getting a faster internet plan won’t fix those Wi-Fi problems. It’s like having a super-fast car but a broken road—it won’t go fast until the road is fixed. First, try improving your Wi-Fi signal using the tips in Chapter 4, then consider a speed upgrade if those don’t help.
Feeling more confident already? That’s the goal!
We know there’s a lot of information here, so we’ve boiled down the most critical troubleshooting steps into easy-to-read, large-print checklists.
Keep them handy next to your modem and router, or by your computer. You can download and print them right now!
Download Your Printable Quick-Fix Checklist Here (PDF)
Remember, technology is here to make your life easier and more enjoyable. With a little knowledge and confidence, you can conquer most internet issues that come your way. And Senior Tech Cafe is always here to help you navigate the digital world with a smile. Explore our other guides for more tips and tricks to empower your tech journey! [Link to Senior Tech Cafe homepageA homepage is the main page of a website—the first thing you see when you visit. It serves as a st... More or main guides section]